"The web was meant to be decentralized"
These words stood out to me as I keenly listened to Angie Jones talk about Web5 at Oscafest in June this year.

The first time I heard about Web5 was last year when I was a newbie highly bullish on Web3, the decentralized future, data ownership, and the Blockchain generally.
Web5 seemed like rocket science to me at that time and I remember reaching out to some people about decentralized identities, Web 3 + 2, and some things I saw in the Web5 pitch from TBD and we were all highly confused because isn't 4 supposed to come after 3? When did we get to 5? 😂

Seeing Angie in Nigeria talk about Web5 was a dream come true and it opened me up to the vast possibilities of this revolutionary tech, Web5. I'll also be opening you up to those possibilities in this article as I aim to show you how Web5 enables decentralized identities and how this can lead to refactoring the web for a more democratic and user-centric future.
By the end of this article, you'll have a deep insight into how Web5 and decentralized identities work, use cases, and advantages and how they can enable refactoring the web by allowing users to switch between different web applications without losing their data and identity. Also, I'll be giving credible pointers on how to get started with Web5 and resources from the TBD team.
Buckle up! We're in for a jolly ride.
What is Web5?
The past four iterations of the World Wide Web have evolved greatly from static web pages to today's interactive experiences. But each step also centralized how we interact and who controls our data. Web5 takes a different path that may change the game.
Remember the early internet when you built your own simple site with HTML and shared info with anyone who typed in your webpage address? That pioneer spirit is what inspired people to imagine what's next. Web1 also known as the "Read-Only Web," let us put ideas out there, but big companies soon took over hosting and functionality.
With Web2, or the "Read-Write Web," came social media, apps, and smartphones - amazing for connecting with others but also consolidating power in just a few giants. They control the platforms and profit handsomely from our data and attention. A few even know us better than we know ourselves! While convenient, many feel this loss of autonomy was not the original vision.
Web3, or the "Read-Write-Own Web," explored decentralizing through blockchains like Bitcoin. Now programs could run without any single point of failure or centralized oversight. But the tech is still maturing and the applications have been niche. Most of us aren't blockchain engineers!
Here is where Web5 comes in, the "Read-Write-Own-Control" web. It takes the best of those prior iterations - individual empowerment, easy sharing, and technological brilliance - without compromising our security or privacy. By using Bitcoin at its core, Web5 puts you in full control of your identity and data.
No longer will others profit off your personal trail. With Web5, you choose what info to store or share, crafting your online presence as uniquely as your real one. Developers create applications that run securely on an open network where no corporate giant like Facebook or Google can censor, exploit, or monopolize your experiences.
Sounds intriguing, no? Web5 aims to restore the original promise of an equitable internet where an individual's voice is as strong as any big player.

Web5 and Decentralized Identities
"We are missing an identity layer"
Angie Jones also stated this, which means decentralized identities are an integral part of Web5.

Your various online profiles are scattered across different sites like pieces of a broken puzzle. All these profiles contain little bits of your identity - your name, interests, friend lists, followers, etc - but the companies hold the full picture. What is missing is a way to unite those puzzle pieces into a coherent identity that you control. With Web5, these pieces can finally fit together in your hands instead of theirs.
So, what are decentralized identities? In simple terms, they are digital identities that are stored and managed on a decentralized network, rather than on a centralized server. This means that instead of relying on a single authority to verify and store your identity, a decentralized system uses a network of nodes to validate and authenticate your information.
But why are decentralized identities so important for Web5? The answer lies in the three pillars of Web5: decentralized identifiers, verifiable credentials, and decentralized web nodes.
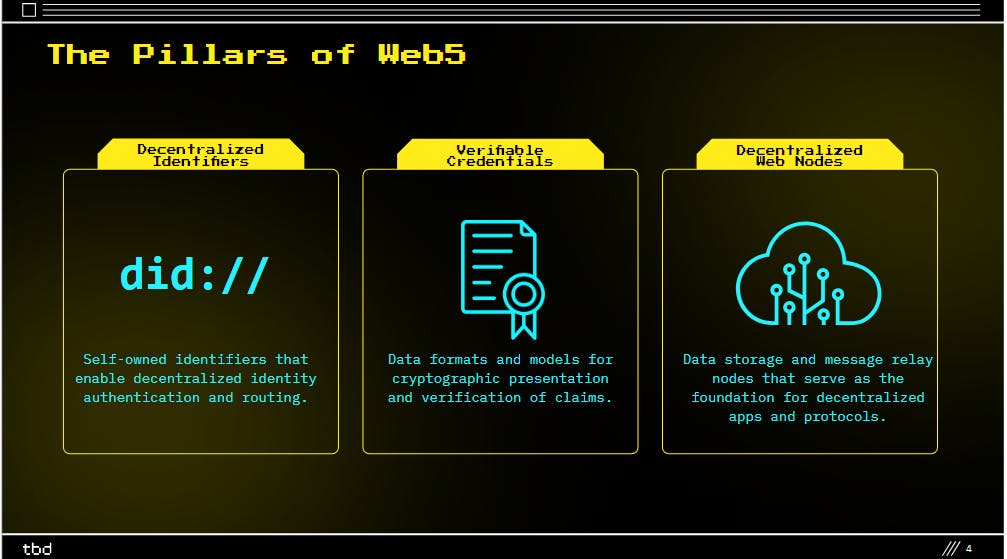
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs): The Foundation of Web5
Decentralized identifiers, or DIDs for short, act like digital passports for your info. Instead of sites having your data, your DID allows you to prove who you are without sharing details. Think of them like crypto keys that unlock your virtual front door from anywhere.
Verifiable Credentials: The Key to Secure Data Sharing
Verifiable credentials take DIDs a step further by letting you choose what "credentials" like your name or email you share, and with whom. You become the CEO of your online profile.
Decentralized Web Nodes: The Future of Data Storage
But how do these credentials get stored and shared in a way that sites and apps can still use them? That's where decentralized nodes come in. Picture your data as families living on their own quiet cul-de-sac (street). Nodes are the friendly neighborhood where everyone knows each other, looks out for one another, and shares what's needed - without nosy landlords watching. Sites connect to these nodes so you control your data neighborhoods from a safe distance.
With these three pillars woven together through open technical standards, Web5 makes it possible for the first time to own your online presence in a way that is fully portable between any application or service.
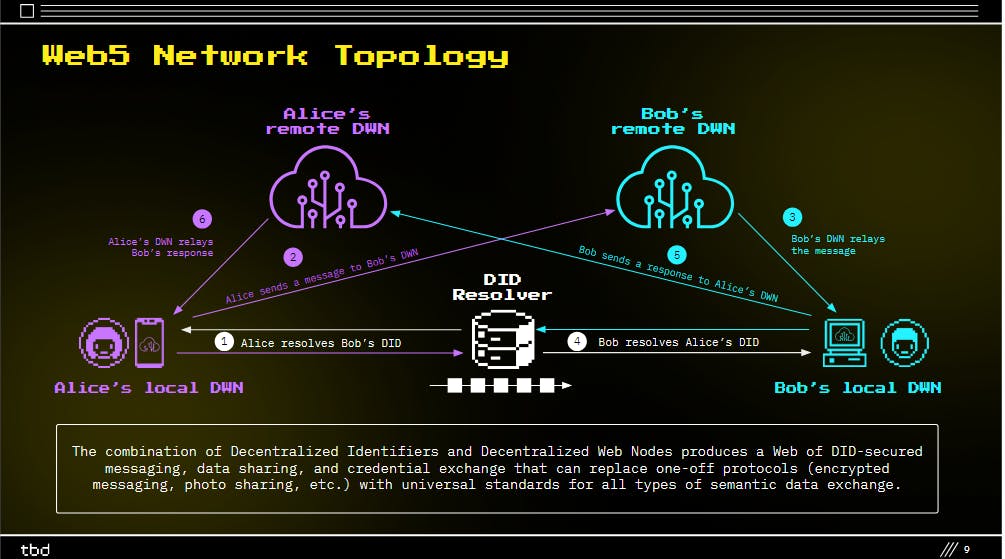
The combination of Decentralized Identifiers and Decentralized Web Nodes produces a Web of DID-secured messaging, data sharing, and credential exchange that can replace one-off protocols (encrypted messaging, photo sharing, etc.) with universal standards for all types of semantic data exchange.
By changing how we think about digital identity at its most basic level, Web5 promises to restore the balance of power on the internet for the benefit of all.
Use Cases of Decentralized Identities
1. Social Media
With a decentralized identity, you can finally separate your online profiles from any single platform. If you decide you want to leave Fakebook one day, you can take your full identity, posts, and friend list with you to another network. No more locking in your data to one company's whims.
2. E-commerce
Online shopping will get a whole lot smoother when your payment info, shipping address, and purchase history aren't scattered across a dozen retailer accounts. With a decentralized identity, all those details can sync seamlessly together so you don't have to re-enter stuff over and over. One sign-in gets you anywhere.
3. Education
For students, verifiable credentials in your decentralized identity can hold all your transcripts, licenses, and diplomas in one place. Need to share your degree with a potential employer? Just click approve and it securely verifies the legitimacy automatically. No more chasing down paper records or making multiple account logins.
4. Healthcare
Sensitive medical information deserves the highest privacy standards but still needs to be accessible in emergencies. By placing your health records like diagnoses, treatments, and medications in your decentralized identity, doctors can review critical info right away if something happens while respecting your consent for access at all times.
Overall, the portable, interoperable nature of decentralized identities makes online life much easier across many industries by putting control and ownership of identity into the user's hands.
How Web5 is Refactoring the Web with The DWP and DWAs Using DIDs and DWNs
One of the key components of Web5 is the Decentralized Web Platform (DWP), a framework that allows developers to build Decentralized Web Apps (DWAs) using Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) and Decentralized Web Nodes (DWNs). Here, you'll find out about the technical jargon behind these terms and how they work together.

DIDs are a new type of identifier that enables verifiable, decentralized digital identity. A DID is a globally unique string that points to a DID document, a set of data that describes the DID subject (the entity that the DID identifies) and the methods that the subject or its delegate can use to prove control over the DID and to interact with others. DIDs are designed to be independent of any centralized registry, identity provider, or certificate authority, and can be created and managed by anyone. DIDs can be used to identify any subject, such as a person, organization, thing, data model, or abstract entity. For example, a DID can identify a user, a device, a website, a document, or a service.
DWNs are a mesh-like data storage and message relay mechanism that enable users to store, discover, and fetch data related to their DIDs and DWAs. DWNs are personal data stores that hold public and encrypted data, such as credentials, preferences, settings, or content. DWNs can also relay messages between users and DWAs, such as requests, responses, notifications, or invitations. Users can operate multiple DWNs that sync to the same state across one another, enabling them to secure, manage, and transact their data with others without relying on location or provider-specific infrastructure, interfaces, or routing mechanisms.
DWAs are web applications that use DIDs and DWNs to provide decentralized identity and data storage capabilities. DWAs can leverage the DWP to create user-centric and trustless experiences, such as social media, gaming, finance, or governance. DWAs can also interoperate with other DWAs and protocols, creating a network effect and a rich ecosystem of decentralized services. DWAs can be accessed through conventional web browsers, with the help of plugins or extensions that enable communication with DIDs and DWNs.
How it all Works: Story of Alice's Empowerment
To illustrate how Web5 is refactoring the web with DWP and DWAs using DIDs and DWNs, let’s imagine a scenario where Alice wants to use a DWA called DecentraChat, a decentralized chat app that allows users to communicate privately and securely with each other.
Alice has a DID that identifies her as a user of DecentraChat. She also has a DWN that stores her DecentraChat profile, contacts, and messages. She does not need to create an account or provide any personal information to DecentraChat, as her identity and data are managed by her DID and DWN.
Alice can use DecentraChat to chat with her friends, who also have DIDs and DWNs. She can send and receive messages, images, videos, or other types of content, which are encrypted and stored in her DWN and the DWNs of her friends. She can also use DecentraChat to discover and join groups or channels, which are identified by DIDs and have their own DWNs.
Alice enjoys using DecentraChat, as she feels more in control and secure about her online communication. She knows that her data and identity are not owned or controlled by any third party and that she can choose whom to share them with. She also knows that her data and identity are portable and interoperable and that she can use them with other DWAs that support the DWP. She can also switch or sync her DWNs across different devices or locations, without losing any data or functionality. She can also update or deactivate her DID or DWN at any time, without affecting the rest of the network.
Web5 is refactoring the web with DWP and DWAs using DIDs and DWNs, creating a more user-centric, trustless, and open web. By using these technologies, users can reclaim their data and identity, and developers can create applications that are more innovative, diverse, and resilient.
Getting Started with Building With Web5
First, you need to understand the basic concepts and components of Web5, such as decentralized identifiers, verifiable credentials, decentralized web nodes, and decentralized web apps as you've learned here then read more about them here:
https://developer.tbd.website/blog/what-is-web5
Documentation
https://developer.tbd.website/docs/ https://developer.tbd.website/docs/web5/quickstart https://developer.tbd.website/api/web5-js
Sample apps
https://developer.tbd.website/docs/web5/build/apps/book-reviews-tutorial https://developer.tbd.website/docs/web5/build/apps/shared-todo-app https://developer.tbd.website/docs/web5/build/apps/dinger-tutorial
This will definitely help you get started with Web5 from zero to hero.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Web5 is set to transform the internet landscape by empowering users through decentralized identities and granting them control over their personal data. By harnessing the power of decentralized identifiers, verifiable credentials, and decentralized web nodes, Web5 paves the way for a more democratic, user-centric web experience. This groundbreaking technology has the potential to reshape a wide range of industries, such as social media, e-commerce, education, and healthcare, ultimately redistributing power and control on the internet to benefit everyone.
As Web5 evolves, it promises to redefine the way we interact online, bringing us closer to the original vision of a truly equitable and decentralized internet.
I hope you enjoyed reading this as much as I enjoyed writing it. See you in the next one!
